|
| |
| Sometimes methods defined in the Collection interfaces don't work |
|
|
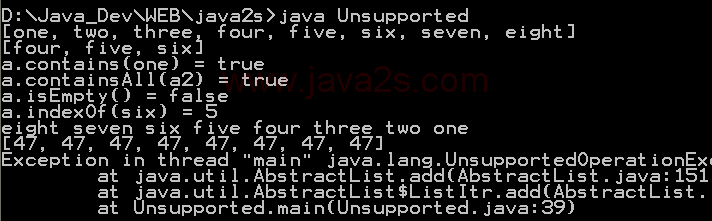 |
|
// : c11:Unsupported.java
// Sometimes methods defined in the Collection interfaces don't work!
// {ThrowsException}
// From 'Thinking in Java, 3rd ed.' (c) Bruce Eckel 2002
// www.BruceEckel.com. See copyright notice in CopyRight.txt.
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ListIterator;
public class Unsupported {
static List a = Arrays.asList("one two three four five six seven eight"
.split(" "));
static List a2 = a.subList(3, 6);
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(a2);
System.out.println("a.contains(" + a.get(0) + ") = "
+ a.contains(a.get(0)));
System.out.println("a.containsAll(a2) = " + a.containsAll(a2));
System.out.println("a.isEmpty() = " + a.isEmpty());
System.out.println("a.indexOf(" + a.get(5) + ") = "
+ a.indexOf(a.get(5)));
// Traverse backwards:
ListIterator lit = a.listIterator(a.size());
while (lit.hasPrevious())
System.out.print(lit.previous() + " ");
System.out.println();
// Set the elements to different values:
for (int i = 0; i < a.size(); i++)
a.set(i, "47");
System.out.println(a);
// Compiles, but won't run:
lit.add("X"); // Unsupported operation
a.clear(); // Unsupported
a.add("eleven"); // Unsupported
a.addAll(a2); // Unsupported
a.retainAll(a2); // Unsupported
a.remove(a.get(0)); // Unsupported
a.removeAll(a2); // Unsupported
}
} ///:~
|
|
|
| Related examples in the same category |
|