| |
| Use Dictionary to record which textbox has been changed and not saved |
|
|
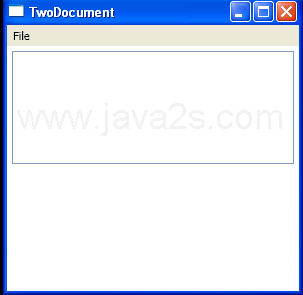 |
<Window x:Class="Commands.TwoDocument"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
Title="TwoDocument" Height="300" Width="300">
<Window.Resources>
<CommandBinding x:Key="binding" Command="ApplicationCommands.Save" Executed="SaveCommand" CanExecute="SaveCommand_CanExecute" />
</Window.Resources>
<Grid>
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto"></RowDefinition>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto"></RowDefinition>
<RowDefinition></RowDefinition>
<RowDefinition></RowDefinition>
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<Menu Grid.Row="0">
<MenuItem Header="File">
<MenuItem Command="New"></MenuItem>
<MenuItem Command="Open"></MenuItem>
<MenuItem Command="Save"></MenuItem>
<MenuItem Command="SaveAs"></MenuItem>
<Separator></Separator>
<MenuItem Command="Close"></MenuItem>
</MenuItem>
</Menu>
<TextBox Margin="5" Grid.Row="2" TextWrapping="Wrap" AcceptsReturn="True" TextChanged="txt_TextChanged">
<TextBox.CommandBindings>
<StaticResource ResourceKey="binding"></StaticResource>
</TextBox.CommandBindings>
</TextBox>
</Grid>
</Window>
//File:Window.xaml.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Controls;
using System.Windows.Data;
using System.Windows.Documents;
using System.Windows.Input;
using System.Windows.Media;
using System.Windows.Media.Imaging;
using System.Windows.Shapes;
namespace Commands
{
public partial class TwoDocument : System.Windows.Window
{
Dictionary<Object, bool> isDirty = new Dictionary<Object, bool>();
public TwoDocument()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void SaveCommand(object sender, ExecutedRoutedEventArgs e)
{
string text = ((TextBox)sender).Text;
isDirty[sender] = false;
}
private void txt_TextChanged(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
isDirty[sender] = true;
}
private void SaveCommand_CanExecute(object sender, CanExecuteRoutedEventArgs e)
{
if (isDirty.ContainsKey(sender) && isDirty[sender] == true)
{
e.CanExecute = true;
}
else
{
e.CanExecute = false;
}
}
}
}
|
|
|
| Related examples in the same category |
| 1. | TextBox Style | |  | | 2. | Bind TextBlock to TextBox | |  | | 3. | TextBox focus listener | |  | | 4. | TextBox with custom ErrorTemplate and ToolTip | |  | | 5. | TextBox uses the ExceptionValidationRule and UpdateSourceExceptionFilter handler | |  | | 6. | TextBox with UpdateSourceExceptionFilter handler | |  | | 7. | TextBox with default ErrorTemplate | |  | | 8. | TextBox MouseLeftButtonDown action and PreviewMouseLeftButtonDown action | |  | | 9. | Assign your own class to DataContent and bind to TextBox | |  | | 10. | Listen to TextBox text changed event | |  | | 11. | Handler for the PreviewKeyDown event on the TextBox | |  | | 12. | TextBox: set text, select all, clear, prepend, insert, append, cut, paste, undo | |  | | 13. | Set TextBox to editable | |  | | 14. | TextBox text changed event | |  | | 15. | TextBox PreviewKeyDown | |  | | 16. | TextBox KeyDown | |  | | 17. | TextBox PreviewKeyUp | | 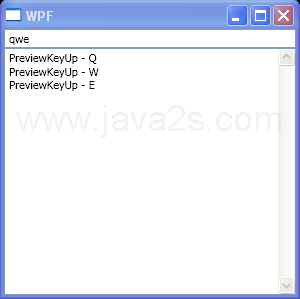 | | 18. | TextBox KeyUp | | 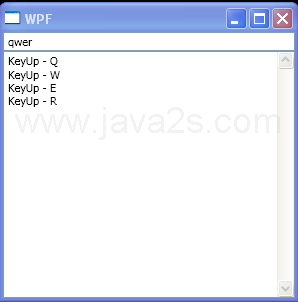 | | 19. | TextBox TextInput | |  | | 20. | TextBox PreviewTextInput | |  | | 21. | Scroll TextBox | |  | | 22. | TextBox TextChanged event | |  | | 23. | Set TextBox ContextMenu to null | |  | | 24. | TextBox Selection start, end and selected text | |  | | 25. | Scrollable TextBox Column | |  | | 26. | TextBox PreviewKeyDown, PreviewKeyUp, PreviewTextInput, KeyDown, KeyUp and TextChanged events | |  | | 27. | Check Spelling Error | |  |
|