|
| |
| A thin wrapper around a List transforming it into a modifiable Set. |
|
|
|
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.AbstractSet;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* A thin wrapper around a <code>List</code> transforming it into a modifiable
* <code>Set</code>.
*
* @version <tt>$Revision: 2800 $</tt>
* @author <a href="mailto:jason@planet57.com">Jason Dillon</a>
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public class ListSet extends AbstractSet implements Set, Cloneable, Serializable {
/** The serialVersionUID */
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7333619218072079496L;
/** The <tt>List</tt> which will be used for element storage. */
protected final List list;
/**
* Construct a <tt>ListSet</tt>.
*
* @param list
* The <tt>List</tt> which will be used for element storage.
*
* @throws IllegalArgumentException
* List is <tt>null</tt> or contains duplicate entries.
*/
public ListSet(final List list) {
if (list == null)
throw new RuntimeException("list");
// make sure there are no duplicates
int size = list.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Object obj = list.get(i);
if (list.indexOf(obj) != list.lastIndexOf(obj)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("list contains duplicate entries");
}
}
this.list = list;
}
/**
* Construct a <tt>ListSet</tt> using an <tt>ArrayList</tt> for backing.
*/
public ListSet() {
this(new ArrayList());
}
/**
* Construct a <tt>ListSet</tt> using an <tt>ArrayList</tt> for backing
* and populated with the given elements.
*
* @param elements
* The elements for the list.
*/
public ListSet(final Collection elements) {
this(new ArrayList(elements));
}
public List getList() {
return list;
}
/**
* Return the size of the set.
*
* @return The size of the set.
*/
public int size() {
return list.size();
}
/**
* Return an iteration over the elements in the set.
*
* @return An iteration over the elements in the set.
*/
public Iterator iterator() {
return list.iterator();
}
/**
* Add an element to the set.
*
* @param obj
* Element to add to the set.
* @return True if the element was added.
*/
public boolean add(final Object obj) {
boolean added = false;
if (!list.contains(obj)) {
added = list.add(obj);
}
return added;
}
/**
* Returns <tt>true</tt> if this set contains no elements.
*
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this set contains no elements.
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return list.isEmpty();
}
/**
* Returns <tt>true</tt> if this set contains the specified element.
*
* @param obj
* Element whose presence in this set is to be tested.
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this set contains the specified element.
*/
public boolean contains(final Object obj) {
return list.contains(obj);
}
/**
* Removes the given element from this set if it is present.
*
* @param obj
* Object to be removed from this set, if present.
* @return <tt>true</tt> if the set contained the specified element.
*/
public boolean remove(final Object obj) {
return list.remove(obj);
}
/**
* Removes all of the elements from this set.
*/
public void clear() {
list.clear();
}
/**
* Returns a shallow copy of this <tt>ListSet</tt> instance.
*
* @return A shallow copy of this set.
*/
public Object clone() {
try {
return super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
throw new InternalError();
}
}
}
|
|
|
| Related examples in the same category |
| 1. | Set, HashSet and TreeSet | | | | 2. | Things you can do with Sets | |  | | 3. | Set operations: union, intersection, difference, symmetric difference, is subset, is superset | | | | 4. | Set implementation that use == instead of equals() | | | | 5. | Set that compares object by identity rather than equality | | | | 6. | Set union and intersection | | | | 7. | Set with values iterated in insertion order. | | | | 8. | Putting your own type in a Set | | 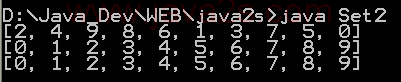 | | 9. | Use set | |  | | 10. | Another Set demo | | | | 11. | Set subtraction | | 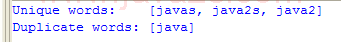 | | 12. | Working with HashSet and TreeSet | | 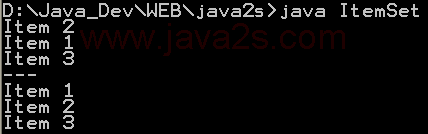 | | 13. | TreeSet Demo | | 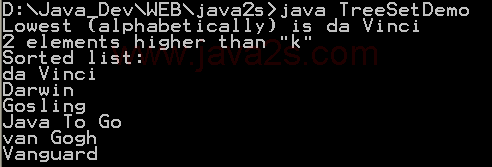 | | 14. | Show the union and intersection of two sets | | | | 15. | Demonstrate the Set interface | | | | 16. | TreeSet Test | | | | 17. | Array Set extends AbstractSet | |  | | 18. | Sync Test | | | | 19. | Set Copy | | | | 20. | Set and TreeSet | | | | 21. | Tail | | | | 22. | What you can do with a TreeSet | |  | | 23. | Remove all elements from a set | | | | 24. | Copy all the elements from set2 to set1 (set1 += set2), set1 becomes the union of set1 and set2 | | | | 25. | Remove all the elements in set1 from set2 (set1 -= set2), set1 becomes the asymmetric difference of set1 and set2 | | | | 26. | Get the intersection of set1 and set2, set1 becomes the intersection of set1 and set2 | | | | 27. | Extend AbstractSet to Create Simple Set | | | | 28. | Int Set | | | | 29. | One Item Set | | | | 30. | Small sets whose elements are known to be unique by construction | | | | 31. | List Set implements Set | | | | 32. | Converts a char array to a Set | | | | 33. | Converts a string to a Set | | | | 34. | Implements the Set interface, backed by a ConcurrentHashMap instance | | | | 35. | An IdentitySet that uses reference-equality instead of object-equality | | | | 36. | An implementation of the java.util.Stack based on an ArrayList instead of a Vector, so it is not synchronized to protect against multi-threaded access. | | | | 37. | A thread-safe Set that manages canonical objects | | |
|