|
| |
| An IdentitySet that uses reference-equality instead of object-equality |
|
|
|
/*
* Copyright 2005 Ralf Joachim
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* An IdentitySet that uses reference-equality instead of object-equality. According
* to its special function it violates some design contracts of the <code>Set</code>
* interface.
*
* @author <a href="mailto:ralf DOT joachim AT syscon DOT eu">Ralf Joachim</a>
* @version $Revision: 7491 $ $Date: 2006-04-13 10:49:49 -0600 (Thu, 13 Apr 2006) $
* @since 0.9.9
*/
public final class IdentitySet implements Set {
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
/** Default number of buckets. */
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 17;
/** Default load factor. */
private static final float DEFAULT_LOAD = 0.75f;
/** Default number of entries. */
private static final int DEFAULT_ENTRIES = (int) (DEFAULT_CAPACITY * DEFAULT_LOAD);
/** Default factor to increment capacity. */
private static final int DEFAULT_INCREMENT = 2;
/** First prime number to check is 3 as we prevent 2 by design. */
private static final int FIRST_PRIME_TO_CHECK = 3;
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
/** Number of buckets. */
private int _capacity;
/** Maximum number of entries before rehashing. */
private int _maximum;
/** Buckets. */
private Entry[] _buckets;
/** Number of map entries. */
private int _entries = 0;
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* Construct a set with default capacity.
*/
public IdentitySet() {
_capacity = DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
_maximum = DEFAULT_ENTRIES;
_buckets = new Entry[DEFAULT_CAPACITY];
}
/**
* Construct a set with given capacity.
*
* @param capacity The capacity of entries this set should be initialized with.
*/
public IdentitySet(final int capacity) {
_capacity = capacity;
_maximum = (int) (capacity * DEFAULT_LOAD);
_buckets = new Entry[capacity];
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
* @see java.util.Collection#clear()
*/
public void clear() {
_capacity = DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
_maximum = DEFAULT_ENTRIES;
_buckets = new Entry[DEFAULT_CAPACITY];
_entries = 0;
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
* @see java.util.Collection#size()
*/
public int size() { return _entries; }
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
* @see java.util.Collection#isEmpty()
*/
public boolean isEmpty() { return (_entries == 0); }
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
* @see java.util.Collection#add(java.lang.Object)
*/
public boolean add(final Object key) {
int hash = System.identityHashCode(key);
int index = hash % _capacity;
if (index < 0) { index = -index; }
Entry entry = _buckets[index];
Entry prev = null;
while (entry != null) {
if (entry.getKey() == key) {
// There is already a mapping for this key.
return false;
}
prev = entry;
entry = entry.getNext();
}
if (prev == null) {
// There is no previous entry in this bucket.
_buckets[index] = new Entry(key, hash);
} else {
// Next entry is empty so we have no mapping for this key.
prev.setNext(new Entry(key, hash));
}
_entries++;
if (_entries > _maximum) { rehash(); }
return true;
}
/**
* Rehash the map into a new array with increased capacity.
*/
private void rehash() {
long nextCapacity = _capacity * DEFAULT_INCREMENT;
if (nextCapacity > Integer.MAX_VALUE) { return; }
nextCapacity = nextPrime(nextCapacity);
if (nextCapacity > Integer.MAX_VALUE) { return; }
int newCapacity = (int) nextCapacity;
Entry[] newBuckets = new Entry[newCapacity];
Entry entry = null;
Entry temp = null;
Entry next = null;
int newIndex = 0;
for (int index = 0; index < _capacity; index++) {
entry = _buckets[index];
while (entry != null) {
next = entry.getNext();
newIndex = entry.getHash() % newCapacity;
if (newIndex < 0) { newIndex = -newIndex; }
temp = newBuckets[newIndex];
if (temp == null) {
// First entry of the bucket.
entry.setNext(null);
} else {
// Hook entry into beginning of the buckets chain.
entry.setNext(temp);
}
newBuckets[newIndex] = entry;
entry = next;
}
}
_capacity = newCapacity;
_maximum = (int) (newCapacity * DEFAULT_LOAD);
_buckets = newBuckets;
}
/**
* Find next prime number greater than minimum.
*
* @param minimum The minimum (exclusive) value of the next prime number.
* @return The next prime number greater than minimum.
*/
private long nextPrime(final long minimum) {
long candidate = ((minimum + 1) / 2) * 2 + 1;
while (!isPrime(candidate)) { candidate += 2; }
return candidate;
}
/**
* Check for prime number.
*
* @param candidate Number to be checked for being a prime number.
* @return <code>true</code> if the given number is a prime number
* <code>false</code> otherwise.
*/
private boolean isPrime(final long candidate) {
if ((candidate / 2) * 2 == candidate) { return false; }
long stop = candidate / 2;
for (long i = FIRST_PRIME_TO_CHECK; i < stop; i += 2) {
if ((candidate / i) * i == candidate) { return false; }
}
return true;
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
* @see java.util.Collection#contains(java.lang.Object)
*/
public boolean contains(final Object key) {
int hash = System.identityHashCode(key);
int index = hash % _capacity;
if (index < 0) { index = -index; }
Entry entry = _buckets[index];
while (entry != null) {
if (entry.getKey() == key) { return true; }
entry = entry.getNext();
}
return false;
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
* @see java.util.Collection#remove(java.lang.Object)
*/
public boolean remove(final Object key) {
int hash = System.identityHashCode(key);
int index = hash % _capacity;
if (index < 0) { index = -index; }
Entry entry = _buckets[index];
Entry prev = null;
while (entry != null) {
if (entry.getKey() == key) {
// Found the entry.
if (prev == null) {
// First element in bucket matches.
_buckets[index] = entry.getNext();
} else {
// Remove the entry from the chain.
prev.setNext(entry.getNext());
}
_entries--;
return true;
}
prev = entry;
entry = entry.getNext();
}
return false;
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
* @see java.util.Collection#iterator()
*/
public Iterator iterator() {
return new IdentityIterator();
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
* @see java.util.Collection#toArray()
*/
public Object[] toArray() {
Object[] result = new Object[_entries];
int j = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < _capacity; i++) {
Entry entry = _buckets[i];
while (entry != null) {
result[j++] = entry.getKey();
entry = entry.getNext();
}
}
return result;
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
* @see java.util.Collection#toArray(java.lang.Object[])
*/
public Object[] toArray(final Object[] a) {
Object[] result = a;
if (result.length < _entries) {
result = (Object[]) java.lang.reflect.Array.newInstance(
result.getClass().getComponentType(), _entries);
}
int j = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < _capacity; i++) {
Entry entry = _buckets[i];
while (entry != null) {
result[j++] = entry.getKey();
entry = entry.getNext();
}
}
while (j < result.length) {
result[j++] = null;
}
return result;
}
/**
* In contrast with the design contract of the <code>Set</code> interface this method
* has not been implemented and throws a <code>UnsupportedOperationException</code>.
*
* {@inheritDoc}
* @see java.util.Set#containsAll
*/
public boolean containsAll(final Collection c) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
/**
* This optional method has not been implemented for <code>IdentitySet</code> instead
* it throws a <code>UnsupportedOperationException</code> as defined in the
* <code>Set</code> interface.
*
* {@inheritDoc}
* @see java.util.Set#addAll
*/
public boolean addAll(final Collection c) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
/**
* This optional method has not been implemented for <code>IdentitySet</code> instead
* it throws a <code>UnsupportedOperationException</code> as defined in the
* <code>Set</code> interface.
*
* {@inheritDoc}
* @see java.util.Set#removeAll
*/
public boolean removeAll(final Collection c) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
/**
* This optional method has not been implemented for <code>IdentitySet</code> instead
* it throws a <code>UnsupportedOperationException</code> as defined in the
* <code>Set</code> interface.
*
* {@inheritDoc}
* @see java.util.Set#retainAll
*/
public boolean retainAll(final Collection c) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* An entry of the <code>IdentitySet</code>.
*/
public final class Entry {
/** Key of entry. */
private Object _key;
/** Identity hashcode of key. */
private int _hash;
/** Reference to next entry. */
private Entry _next = null;
/**
* Construct an entry.
*
* @param key Key of entry.
* @param hash Identity hashcode of key.
*/
public Entry(final Object key, final int hash) {
_key = key;
_hash = hash;
}
/**
* Get key of entry.
*
* @return Key of entry.
*/
public Object getKey() { return _key; }
/**
* Get identity hashcode of key.
*
* @return Identity hashcode of key.
*/
public int getHash() { return _hash; }
/**
* Set reference to next entry.
*
* @param next New reference to next entry.
*/
public void setNext(final Entry next) { _next = next; }
/**
* Get reference to next entry.
*
* @return Reference to next entry.
*/
public Entry getNext() { return _next; }
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* An iterator over all entries of the <code>IdentitySet</code>.
*/
private class IdentityIterator implements Iterator {
/** Index of the current bucket. */
private int _index = 0;
/** The next entry to be returned. <code>null</code> when there is none. */
private Entry _next = _buckets[0];
/**
* Construct a iterator over all entries of the <code>IdentitySet</code>.
*/
public IdentityIterator() {
if (_entries > 0) {
while ((_next == null) && (++_index < _capacity)) {
_next = _buckets[_index];
}
}
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
* @see java.util.Iterator#hasNext()
*/
public boolean hasNext() {
return (_next != null);
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
* @see java.util.Iterator#next()
*/
public Object next() {
Entry entry = _next;
if (entry == null) { throw new NoSuchElementException(); }
_next = entry.getNext();
while ((_next == null) && (++_index < _capacity)) {
_next = _buckets[_index];
}
return entry.getKey();
}
/**
* This optional method is not implemented for <code>IdentityIterator</code>
* instead it throws a <code>UnsupportedOperationException</code> as defined
* in the <code>Iterator</code> interface.
*
* @see java.util.Iterator#remove()
*/
public void remove() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
}
|
|
|
| Related examples in the same category |
| 1. | Set, HashSet and TreeSet | | | | 2. | Things you can do with Sets | |  | | 3. | Set operations: union, intersection, difference, symmetric difference, is subset, is superset | | | | 4. | Set implementation that use == instead of equals() | | | | 5. | Set that compares object by identity rather than equality | | | | 6. | Set union and intersection | | | | 7. | Set with values iterated in insertion order. | | | | 8. | Putting your own type in a Set | | 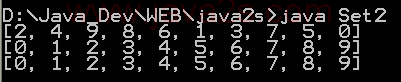 | | 9. | Use set | |  | | 10. | Another Set demo | | | | 11. | Set subtraction | | 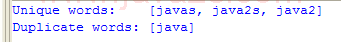 | | 12. | Working with HashSet and TreeSet | | 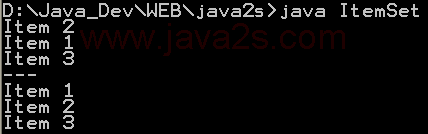 | | 13. | TreeSet Demo | | 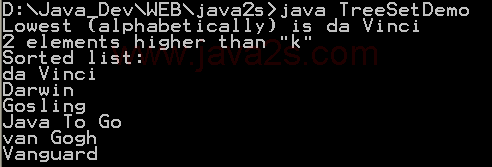 | | 14. | Show the union and intersection of two sets | | | | 15. | Demonstrate the Set interface | | | | 16. | TreeSet Test | | | | 17. | Array Set extends AbstractSet | | 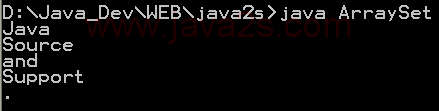 | | 18. | Sync Test | | | | 19. | Set Copy | | | | 20. | Set and TreeSet | | | | 21. | Tail | | | | 22. | What you can do with a TreeSet | |  | | 23. | Remove all elements from a set | | | | 24. | Copy all the elements from set2 to set1 (set1 += set2), set1 becomes the union of set1 and set2 | | | | 25. | Remove all the elements in set1 from set2 (set1 -= set2), set1 becomes the asymmetric difference of set1 and set2 | | | | 26. | Get the intersection of set1 and set2, set1 becomes the intersection of set1 and set2 | | | | 27. | Extend AbstractSet to Create Simple Set | | | | 28. | Int Set | | | | 29. | One Item Set | | | | 30. | Small sets whose elements are known to be unique by construction | | | | 31. | List Set implements Set | | | | 32. | Converts a char array to a Set | | | | 33. | Converts a string to a Set | | | | 34. | Implements the Set interface, backed by a ConcurrentHashMap instance | | | | 35. | An implementation of the java.util.Stack based on an ArrayList instead of a Vector, so it is not synchronized to protect against multi-threaded access. | | | | 36. | A thin wrapper around a List transforming it into a modifiable Set. | | | | 37. | A thread-safe Set that manages canonical objects | | |
|